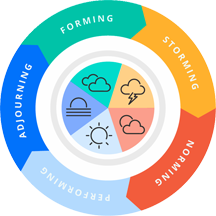
Tuckman's stages of group development. Adding or removing members to the group during the course of its efforts to reach agreement can delay the achievement by causing the group to restart its path through the stages of group development. Bring together everyone you think you'll need from the outset, and keep them together until you have agreement. Image (cc) Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International license by DovileMi, courtesy Wikimedia.
Reaching agreements about matters in technological contexts requires an approach that's similar to — but different from — reaching agreements in other contexts. Most of what's most readily available as guidelines for reaching agreements has been developed for other contexts, such as negotiations related to business formation, exchanges of assets, divorce, or matters of law. And these patterns can be helpful in technological contexts if suitably adapted. The key phrase here is suitably adapted. In this post I explore some of the distinguishing characteristics of technological contexts that make reaching agreements so challenging.
What a technological context is
For this purpose, a technological context is one primarily defined by a set of technological elements, either physical or conceptual. Examples of technological elements are devices or systems that exhibit behaviors or possess properties that are relevant to the disagreement, and which can be understood in terms of engineering or applied science. Another example is a representation of such a device or system, in combinations of diagrams, figures, and text.
The property of being technological is one of degree. The degree of importance of understanding the relevant engineering or applied science principles determines how technological the context is. Usually, and unfortunately, assessing the importance of such understanding requires a high level of that same understanding.
For example, a discussion regarding the weight-bearing capacity of a concrete driveway is a fairly technological context. By contrast, a discussion regarding sweeping leaves from that same concrete driveway is less likely to be a technological context.
How troubles arise in technological contexts
Attributes of Attributes of technological contexts
that are especially troublesome are
those that challenge interpersonal
skills of group memberstechnological contexts that are especially troublesome are those that challenge the interpersonal skills of group members. Difficulties arise, in part, when people believe they are conversing about a purely technical issue when they are actually confronting an issue that is essentially political or interpersonal. Below are three such attributes of technological contexts that create risks for groups seeking to reach agreement.
- Breadth of knowledge
- The knowledge required of a group involved in technical negotiations can be very broad indeed. In some situations the set of interacting technical artifacts can include items that are the responsibility of other groups or other enterprises. Or it can include legacy items developed long ago. In such cases, members of other groups or organizations might be detailed to participate in the negotiations as consulting experts. Or members of the group might be asked to "cram" a knowledge domain to help the group broaden its base of expertise.
- Adding new members to a group — or removing members when you believe they've completed their work — can cause the group to traverse again several of the five stages of Tuckman's model of small group development. [Tuckman & Jensen 1977] This re-traversal can delay the arrival of agreement because it causes the group to revisit interpersonal issues that it had previously resolved.
- If you anticipate the need to involve additional people, you can speed agreement by including them from the outset, rather than adding them only "when we really need their expertise."
- Rapid evolution of domain knowledge
- Rapid evolution of the relevant body of knowledge has two effects on groups as they reach for agreement. First, members must devote significant time and effort to maintaining their own knowledge currency. This workload can be so burdensome that members are compelled to be selective about what parts of the knowledge base they attend to carefully.
- Second, members' personal grasp of relevant issues might not be synchronized. That is, some members might be aware of and have a grasp of a relevant change or innovation, while others might not.
- When debates erupt, the first thing to check is the uniformity of knowledge currency across the group's members. The points of disagreement can often vanish when everyone becomes current.
- Social skills deficits
- "Soft skills" is a term that denotes a cluster of personal traits and abilities that enable members of social groups to form and maintain strong relationships. These skills include social facility, empathy, communication (reading, writing, speaking, and listening), teamwork, leadership, critical thinking, literacy, numeracy, trustworthiness, and more.
- Higher educational institutions do emphasize preparing graduates for dealing with the technical components of technological contexts. But they tend not to emphasize soft skill development to an analogous extent. [Matteson, et al. 2016] This bias is perhaps most evident in the education of students aiming for careers in technology.
- Organizations that depend for their success on the technical skills of their employees would do well to install and pursue a long-term program for soft skills development of all employees.
Last words
There are certainly many more attributes of technological contexts that create risks for groups seeking agreement about issues they face. For example, knowledge deficits in management ranks can cause managers to impose unreasonable or even irreconcilable constraints on teams that are engaged in problem solving. And because some organizations keep outmoded devices or practices in service alongside more modern components, enterprise asset bases are unnecessarily heterogeneous. That heterogeneity extends the persistence of the need for otherwise-obsolete knowledge for groups that must attend to those assets.
When teams have difficulty reaching agreements in technological contexts, the root cause might lie not in the team or its members, but in the context in which they work. ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Are you fed up with tense, explosive meetings? Are you or a colleague the target of a bully? Destructive conflict can ruin organizations. But if we believe that all conflict is destructive, and that we can somehow eliminate conflict, or that conflict is an enemy of productivity, then we're in conflict with Conflict itself. Read 101 Tips for Managing Conflict to learn how to make peace with conflict and make it an organizational asset. Order Now!
More about Tuckman's sequence of small group development
 The Politics of Forming Joint Leadership Teams [January 4, 2023]
The Politics of Forming Joint Leadership Teams [January 4, 2023]- Some teams, business units, or enterprises are led not by individuals, but by joint leadership teams of two or more. They face special risks that arise from both the politics of the joint leadership team and the politics of the organization hosting it.
 Tuckman's Model and Joint Leadership Teams [January 18, 2023]
Tuckman's Model and Joint Leadership Teams [January 18, 2023]- Tuckman's model of the stages of group development, applied to Joint Leadership Teams, reveals characteristics of these teams that signal performance levels less than we hope for. Knowing what to avoid when we designate these teams is therefore useful.
 White Water Rafting as a Metaphor for Group Development [December 4, 2024]
White Water Rafting as a Metaphor for Group Development [December 4, 2024]- Tuckman's model of small group development, best known as "Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing," applies better to development of some groups than to others. We can use a metaphor to explore how the model applies to Storming in task-oriented work groups.
 Subgrouping and Conway's Law [December 18, 2024]
Subgrouping and Conway's Law [December 18, 2024]- When task-oriented work groups address complex tasks, they might form subgroups to address subtasks. The structure of the subgroups and the order in which they form depend on the structure of the group's task and the sequencing of the subtasks.
 The Storming Puzzle: I [December 25, 2024]
The Storming Puzzle: I [December 25, 2024]- Tuckman's model of small group development, best known as "Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing," applies to today's task-oriented work groups — if we adapt our understanding of it. If we don't adapt, the model appears to conflict with reality.
 The Storming Puzzle: II [January 1, 2025]
The Storming Puzzle: II [January 1, 2025]- For some task-oriented work groups, Tuckman's model of small group development doesn't seem to fit. Storming seems to be absent, or Storming never ends. To learn how this illusion forms, look closely at Satir's Change Model and at what we call a task-oriented work group.
 The Storming Puzzle: Six Principles [January 8, 2025]
The Storming Puzzle: Six Principles [January 8, 2025]- For some task-oriented work groups, Tuckman's model of small group development seems not to fit. Storming seems to be either absent or continuous. To learn how this illusion forms, look closely at the processes that can precipitate episodes of Storming in task-oriented work groups.
 The Storming Puzzle: Patterns and Antipatterns [January 15, 2025]
The Storming Puzzle: Patterns and Antipatterns [January 15, 2025]- Tuckman's model of small group development, best known as "Forming-Storming-Norming-Performing," applies to today's task-oriented work groups, if we understand the six principles that govern transitions from one stage to another. Here are some examples.
 Storming: Obstacle or Pathway? [January 22, 2025]
Storming: Obstacle or Pathway? [January 22, 2025]- The Storming stage of Tuckman's model of small group development is widely misunderstood. Fighting the storms, denying they exist, or bypassing them doesn't work. Letting them blow themselves out in a somewhat-controlled manner is the path to Norming and Performing.
 A Framework for Safe Storming [January 29, 2025]
A Framework for Safe Storming [January 29, 2025]- The Storming stage of Tuckman's development sequence for small groups is when the group explores its frustrations and degrees of disagreement about both structure and task. Only by understanding these misalignments is reaching alignment possible. Here is a framework for this exploration.
 On Shaking Things Up [February 5, 2025]
On Shaking Things Up [February 5, 2025]- Newcomers to work groups have three tasks: to meet and get to know incumbent group members; to gain their trust; and to learn about the group's task and how to contribute to accomplishing it. General skills are necessary, but specifics are most important.
 On Substituting for a Star [February 12, 2025]
On Substituting for a Star [February 12, 2025]- Newcomers to work groups have three tasks: to meet and get to know incumbent group members; to gain their trust; and to learn about the group's task and how to contribute to accomplishing it. All can be difficult; all are made even more difficult when the newcomer is substituting for a star.
Footnotes
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenfHlRlTgqCIXkUHBTner@ChacrEuHRQPYVKkOucGfoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Effective Meetings:
 Dispersed Teams and Latent Communications
Dispersed Teams and Latent Communications- When geography divides a team, conflicts can erupt along the borders. "Us" and "them"
becomes a way of seeing the world, and feelings about people at other sites can become hostile. Why
does this happen and what can we do about it?
 Finding the Third Way
Finding the Third Way- When a team is divided, and agreement seems out of reach, attempts to resolve the conflict usually focus
on the differences between the contrasting positions. Focusing instead on their similarities can be
a productive technique for reaching agreement.
 The End-to-End Cost of Meetings: I
The End-to-End Cost of Meetings: I- By now, most of us realize how expensive meetings are. Um, well, maybe not. Here's a look at some of
the most-often overlooked costs of meetings.
 Polychronic Meetings
Polychronic Meetings- In very dynamic contexts, with multiple issues to address, we probably cannot rely on the usual format
of single-threaded meeting with a list of agenda items to be addressed each in their turn. A more flexible,
issue-driven format might work better.
 Workplace Politics and Social Exclusion: II
Workplace Politics and Social Exclusion: II- In workplace politics, social exclusion can be based on the professional role of the target, the organizational
role of the target, or personal attributes of the target. Each kind has its own effects. Each requires
specific responses.
See also Effective Meetings and Effective Meetings for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming April 30: On Planning in Plan-Hostile Environments: II
Coming April 30: On Planning in Plan-Hostile Environments: II- When we finally execute plans, we encounter obstacles. So we find workarounds or adjust the plans. But there are times when nothing we try gets us back on track. When this happens for nearly every plan, we might be working in a plan-hostile environment. Available here and by RSS on April 30.
 And on May 7: Subject Matter Bullying
And on May 7: Subject Matter Bullying- Most workplace bullying tactics have analogs in the schoolyard — isolation, physical attacks, name-calling, and rumor-mongering are common examples. Subject matter bullying might be an exception, because it requires expertise in a sophisticated knowledge domain. And that's where trouble begins. Available here and by RSS on May 7.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenfHlRlTgqCIXkUHBTner@ChacrEuHRQPYVKkOucGfoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenfHlRlTgqCIXkUHBTner@ChacrEuHRQPYVKkOucGfoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!