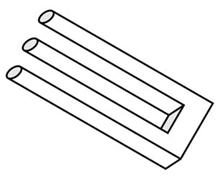
The Impossible Trident visual paradox, a member of the class of drawings known as impossible objects or optical illusions. Read about the history of this impossible object.
Politics plays a paradoxical role in rescheduling work because it can be both the cause of the need to reschedule, and the means by which we meet that need. Image (cc) by SA 4.0 and courtesy ByrdSeed LLC.
Organizational politics is what happens when we contend with each other for control or dominance, or when we work together to solve shared problems. Rescheduling collaborative work is one activity in which organizational politics plays two critical roles. The role that perhaps comes to mind first is cooperative political behavior. Cooperative political behavior is behavior in which we influence others — and allow others to influence us — to shift control of resources needed for producing the desired results.
A second role for political behavior related to rescheduling is perhaps less widely acknowledged. That role includes anti-cooperative political behavior. Anti-cooperative Although political behavior accounts for much of
our ability to reschedule when we need to, it
also accounts for much of the need to reschedulepolitical behavior is behavior in which we set our own parochial concerns ahead of others' concerns in order to achieve our own objectives. We do this even though — or sometimes because — we recognize that this choice can prevent others from achieving their objectives.
Anti-cooperative political behavior is relevant to rescheduling because it's often the source of the need to reschedule. Thus, although political behavior accounts for much of our ability to reschedule when we need to, it also accounts for much of the need to reschedule.
The paradox of the politics of scheduling
Politics thus has a paradoxical contribution to organizational scheduling. This paradox can seem at first to condemn organizations to an unending struggle to stamp out politics, but it actually provides a path to resolving itself.
Politics provides a resolution to this paradox as follows. If the people of an organization can acquire political mastery, they can guide their anti-cooperative behavior so as to reduce its harmful effects. And likewise, they can guide their cooperative behavior so as to enhance its beneficial effects.
Last words
To understand how to guide political behavior, we can examine that behavior at two scales. At the direct scale we make political choices that directly affect how one person (or one organizational unit) collaborates with one other person (or one other organizational unit). At the system scale, we make political choices that affect how systems of people or organizational units collaborate. Next time we'll survey those choices and the consequences of each, both at the direct scale and the system scale. ![]() Next issue in this series
Next issue in this series ![]() Top
Top ![]() Next Issue
Next Issue
Is every other day a tense, anxious, angry misery as you watch people around you, who couldn't even think their way through a game of Jacks, win at workplace politics and steal the credit and glory for just about everyone's best work including yours? Read 303 Secrets of Workplace Politics, filled with tips and techniques for succeeding in workplace politics. More info
Your comments are welcome
Would you like to see your comments posted here? rbrenfHlRlTgqCIXkUHBTner@ChacrEuHRQPYVKkOucGfoCanyon.comSend me your comments by email, or by Web form.About Point Lookout
 Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
Thank you for reading this article. I hope you enjoyed it and
found it useful, and that you'll consider recommending it to a friend.
This article in its entirety was written by a human being. No machine intelligence was involved in any way.
Point Lookout is a free weekly email newsletter. Browse the archive of past issues. Subscribe for free.
Support Point Lookout by joining the Friends of Point Lookout, as an individual or as an organization.
Do you face a complex interpersonal situation? Send it in, anonymously if you like, and I'll give you my two cents.
Related articles
More articles on Workplace Politics:
 Devious Political Tactics: A Field Manual
Devious Political Tactics: A Field Manual- Some practitioners of workplace politics use an assortment of devious tactics to accomplish their ends.
Since most of us operate in a fairly straightforward manner, the devious among us gain unfair advantage.
Here are some of their techniques, and some suggestions for effective responses.
 The Risky Role of Hands-On Project Manager
The Risky Role of Hands-On Project Manager- The hands-on project manager manages the project and performs some of the work, too. There are lots
of excellent hands-on project managers, but the job is inherently risky, and it's loaded with potential
conflicts of interest.
 How to Create Distrust
How to Create Distrust- A trusting environment is critical to high performance. That's why it's important to recognize behaviors
that erode trust in others. Here's a little catalog of methods people use — intentionally or not
— to create distrust.
 Behavioral Indicators of Political Risk
Behavioral Indicators of Political Risk- Avoiding dangerous political interactions is easier if you know what to look for. Among the indicators
of possible trouble are the behaviors of the people around you.
 Columbo Tactics: II
Columbo Tactics: II- This is Part II of a series showing how the less powerful can adapt the tactics of TV detective Lt.
Columbo when they're interacting with the more powerful.
See also Workplace Politics and Workplace Politics for more related articles.
Forthcoming issues of Point Lookout
 Coming April 30: On Planning in Plan-Hostile Environments: II
Coming April 30: On Planning in Plan-Hostile Environments: II- When we finally execute plans, we encounter obstacles. So we find workarounds or adjust the plans. But there are times when nothing we try gets us back on track. When this happens for nearly every plan, we might be working in a plan-hostile environment. Available here and by RSS on April 30.
 And on May 7: Subject Matter Bullying
And on May 7: Subject Matter Bullying- Most workplace bullying tactics have analogs in the schoolyard — isolation, physical attacks, name-calling, and rumor-mongering are common examples. Subject matter bullying might be an exception, because it requires expertise in a sophisticated knowledge domain. And that's where trouble begins. Available here and by RSS on May 7.
Coaching services
I offer email and telephone coaching at both corporate and individual rates. Contact Rick for details at rbrenfHlRlTgqCIXkUHBTner@ChacrEuHRQPYVKkOucGfoCanyon.com or (650) 787-6475, or toll-free in the continental US at (866) 378-5470.
Get the ebook!
Past issues of Point Lookout are available in six ebooks:
- Get 2001-2 in Geese Don't Land on Twigs (PDF, )
- Get 2003-4 in Why Dogs Wag (PDF, )
- Get 2005-6 in Loopy Things We Do (PDF, )
- Get 2007-8 in Things We Believe That Maybe Aren't So True (PDF, )
- Get 2009-10 in The Questions Not Asked (PDF, )
- Get all of the first twelve years (2001-2012) in The Collected Issues of Point Lookout (PDF, )
Are you a writer, editor or publisher on deadline? Are you looking for an article that will get people talking and get compliments flying your way? You can have 500-1000 words in your inbox in one hour. License any article from this Web site. More info
Follow Rick
Recommend this issue to a friend
Send an email message to a friend
rbrenfHlRlTgqCIXkUHBTner@ChacrEuHRQPYVKkOucGfoCanyon.comSend a message to Rick
![]() A Tip A Day feed
A Tip A Day feed
![]() Point Lookout weekly feed
Point Lookout weekly feed
 My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!
My blog, Technical Debt for Policymakers, offers
resources, insights, and conversations of interest to policymakers who are concerned with managing
technical debt within their organizations. Get the millstone of technical debt off the neck of your
organization!